Author Archives: libudas
CVS Server Installation/Configuration
A Simple CVS Server Install/Configuration In 15 minutes
Introduction :
CVS is a version control system, an important component of Source Configuration Management (SCM). Using it, you can record the history of sources files, and documents. It fills a similar role to the free software RCS, PRCS, and Aegis packages.
CVS is a production quality system in wide use around the world, including many free software projects.
While CVS stores individual file history in the same format as RCS, it offers the following significant advantages over RCS:
- It can run scripts which you can supply to log CVS operations or enforce site-specific polices.
- Client/server CVS enables developers scattered by geography or slow modems to function as a single team. The version history is stored on a single central server and the client machines have a copy of all the files that the developers are working on. Therefore, the network between the client and the server must be up to perform CVS operations (such as checkins or updates) but need not be up to edit or manipulate the current versions of the files. Clients can perform all the same operations which are available locally.
- In cases where several developers or teams want to each maintain their own version of the files, because of geography and/or policy, CVS‘s vendor branches can import a version from another team (even if they don’t use CVS), and then CVS can merge the changes from the vendor branch with the latest files if that is what is desired.
- Unreserved checkouts, allowing more than one developer to work on the same files at the same time.
- CVS provides a flexible modules database that provides a symbolic mapping of names to components of a larger software distribution. It applies names to collections of directories and files. A single command can manipulate the entire collection.
- CVS servers run on most unix variants, and clients for Windows NT/95, OS/2 and VMS are also available. CVS will also operate in what is sometimes called server mode against local repositories on Windows 95/NT.
Installation :
Step 1: yum install cvs*
Step 2: yum install xinetd
Step 3: Create cvs users & create a group say cvsgroup to which we add all cvs users.
#groupadd cvsgroup #useradd –G cvsgroup sandy #passwd sandyStep 4: Create a cvs directory say /data with proper permissions and owner ship.
#mkdir /data #chmod ug+rwx /data #chgrp cvsgroup /dataStep 5: Flag /data directory with SGID bit, so the group permissions will be inherited to files and folders created under /data directory.
#chmod g+s /data
Step 6: Edit /etc/xinet.d/cvs with the below details
service cvspserver { disable = no port = 2401 socket_type = stream protocol = tcp wait = no user = root group = cvsgroup passenv = PATH server = /usr/bin/cvs env = HOME=/data server_args = -f –allow-root=/data/repository1 –allow-root=/data/repository2 pserver }Step 7: Restart the xinetd service.
# service xinetd star
Step 8: Initialize the repositories
# cvs -d /data/repostory1 init
# cvs -d /data/repostory2 init
Step 9: Normal Linux users on CVS Server can now be able to login to CVS server using username/password depending on which Client tool you prefer.
Refererence: The Below Links For More Details
Samba file Server Installation and configuration on Centos 6.2
Samba file Server
Samba is software that can be run on a platform other than Microsoft Windows, for example, UNIX, Linux, IBM System 390, OpenVMS, and other operating systems. Samba uses the TCP/IP protocol that is installed on the host server. When correctly configured, it allows that host to interact with a Microsoft Windows client or server as if it is a Windows file and print server.
From http://www.samba.org
Prerequisites
1. Disable Selinux
Selinux can be disabled temporarily or permanently
a. Temporarily
# setenforce 0
b. Permanently
Edit /etc/sysconfig/selinux and set SELINUX entry to disabled
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing – SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive – SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled – No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted – Targeted processes are protected,
# mls – Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
This needs a server restart to take effect.
2. Disable or add rules to iptables
a. Disable iptables ( Not Recommended)
#service iptables stop
#chkconfig –level 345 iptables off {disable iptable service on server startup}
b. Add rules to allow samba ports for communication.
# iptables -A INPUT i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport –dports 137,138,139,445 -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# service iptables save
Installation
1. Yum install samba samba-client samba-common cups-libs.
This will install samba server and dependencies.
2. After Installation a default file configuration file will be created on /etc/samba/smb.conf.
3. Star the service and flag it for automatic restart on sever reboot.
#service smb start
#chkconfig – -level 35 smb on
4. Now backup your original smb.conf file and we will discuss some simple to complex share definitions.
Smb.conf file is main configuration file of samba file server. The file is organised as sections & Parameters. Some default sections on a samba configuration files are
[global]
The parameters defined in global section apply to the whole server.
[homes]
The parameters defined on this section are useful for samba users connecting to their home share.
[printers]
For printers specific parameters
Now we can have look at few smb.conf files for different purposes
1. A sample smb.conf file for file sharing without username/password
a. Edit /etc/samba/smb.conf with below details(Customise according to your environment)
[global] workgroup = MYGROUP server string = Samba Server Version %v log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m max log size = 50 dns proxy = No cups options = raw security = share guest account = nobody [homes] comment = Home Directories read only = No browseable = No [shared] comment = Shared Stuff path = /shared/ read only = No guest ok = Yesb. Create a directory shared with proper permissions.
#mkdir /shared; chmod ugo=rwx /shared
c. Use testparm command to test the configuration file. And restart the service.
d. Now you will be able to access the share from windows.
2. A fully fledged samba share server with recycle bin capabilities.
- Samba share(public) accessible to configured users & secured using username/password
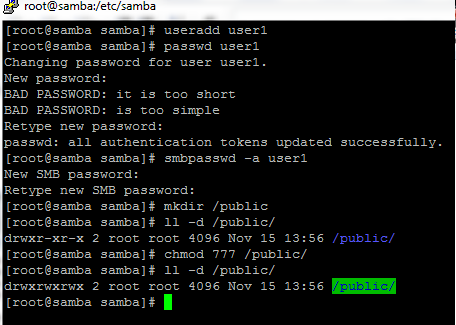
- Create a Linux user name say user1 & add to samba users.
- Create folder say /public which will be shared by the users.
- Flag it with appropriate permissions so anyone with access to the share has read/write permissions.
- Edit smb.conf with the following details
[global]
workgroup = MYGROUP
server string = Samba Server Version %v
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
dns proxy = No
cups options = raw
security = user
passdb backend = tdbsam
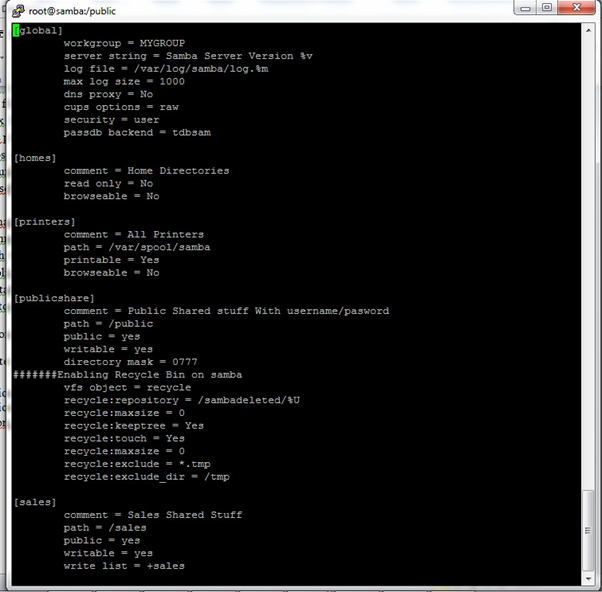
[publicshare]
comment = Public Shared stuff With username/pasword
path = /public
public = yes
writable = yes
directory mask = 0777
Smb.conf explanation
Log_file == will create a log file under /var/log/samba/log.pcnameaccessing
max log size ==This option (an integer in kilobytes) specifies the max size the log file should grow to. Samba periodically checks the size and if it is exceeded it will rename the file, adding a .old extension,A size of 0 means no limit.
security & passdb backend == Backend to store user information in. New installations should use either tdbsam or ldapsam. smbpasswd is available for backwards compatibility. tdbsam requires no further configuration.
directory mask== enable to create a directory inside another user created directory(fully writable)
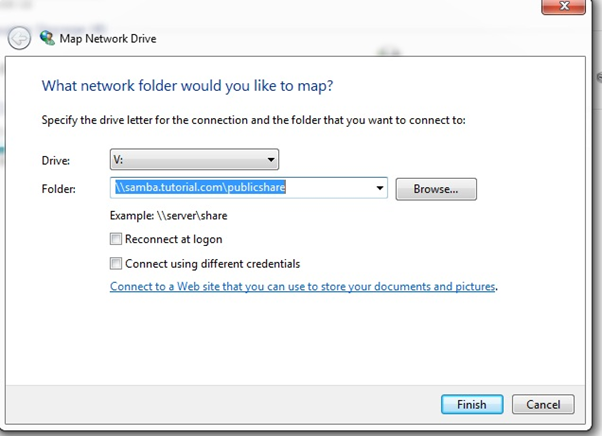
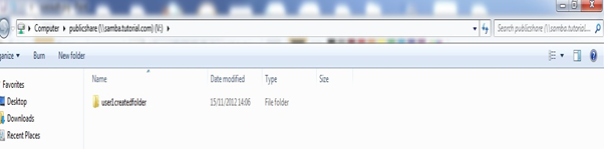
- Access for the share from windows using username/password created above.
- Samba share (sales) accessible to a group of users.
- Create Linux users say sales1 & sales 2, create a group called sales and add the above users to the group sales. Add the users to samba
- Make directory /sales with proper permissions and ownership (flag it with SGID bit so group of the parent directory will be inherited to files created in sales directory.
- Edit smb.conf with the following details
[sales]
comment = Sales Shared Stuff
path = /sales
public = yes
writable = yes
write list = +sales
create mask = 0774
directory mask = 0775
Smb.conf explanation
write list == This is a list of users that are given read-write access to a service. If the connecting user is in this list then they will be given write access, no matter what the read only option is set to. The list can include group names using the +group syntax.(In older Samba version syntax was @groupname)
- Access for the share from windows using username/password created above.
Sales1
- SGID permission inherited from Parent directory & directory mask variable in action.
- Samba home share for each user.
Edit smb.conf with the following details
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
read only = No
browseable = No
- Access for the home share from windows using username/password .
- Recycle bin capabilities on public share.
Recycle bin is a nice feature in samba, which helps to retrieve user deleted files very easily. By configuring this option the deleted files are actually moved rather than deleted to a directory specified at smb.conf.
- Make a directory say sambadeleted and flag with proper permission.
- Edit smb.conf file with following details.
[publicshare]
comment = Public Shared stuff With username/pasword
path = /public
public = yes
writable = yes
directory mask = 0777
#######Enabling Recycle Bin on samba
vfs object = recycle
recycle:repository = /sambadeleted/%U
recycle:versions = Yes
recycle:keeptree = Yes
recycle:touch = Yes
recycle:maxsize = 0
recycle:exclude = *.tmp
recycle:exclude_dir = /tmp
Smb.conf explanation
recycle:keeptree==preserve directory structure.
recycle:touch== Specifies whether a file’s access date should be updated when the file is moved to the repository.
recycle:maxsize== This option (an integer in kilobytes) specifies the max size the recycled file,A size of 0 means no limit
recycle:repository== . sambadeleted /%U
This specifies where the deleted files will be stored. Therefore anything that is deleted is moved to the directory /sambadeleted. The %U variable is the username of the person currently browsing the share. So for every user that deletes a file there is a directory with their username containing all the files they have deleted.
Refer the link for more details: http://www.samba.org/samba/docs/man/manpages-3/vfs_recycle.8.html
For example:
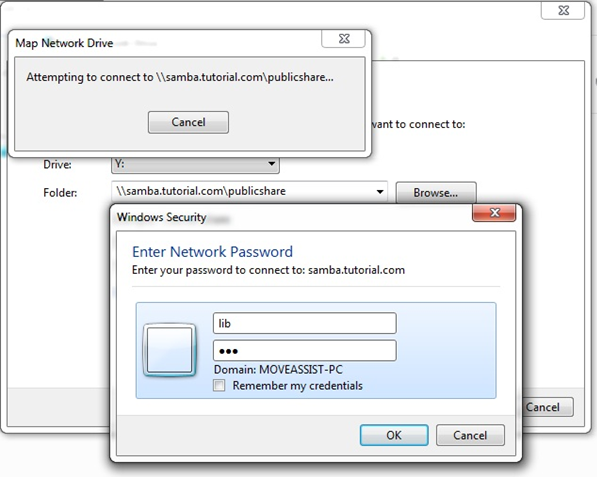
- Map the publicshare using lib and sandy as username and create folders createdbylib & createdbysandy respectively. Drop some files in the folders.
- Delete the folders from the shares(lib can delete folder created by sandy & sandy can delete folder created by lib)
- Now check the /sambadeleted directory from server to verify recycle bin functionality
Note : /sambadeleted directory should be created prior and should have proper write permissions for all users
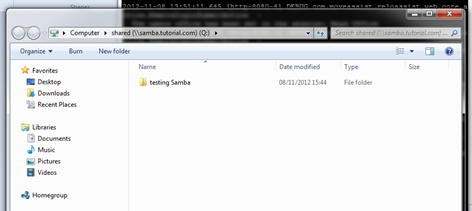
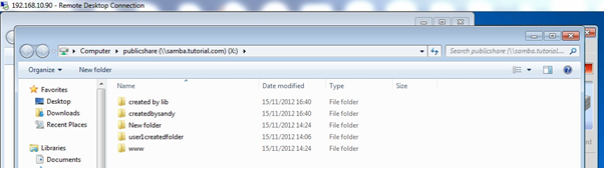
- The screen shot shows the files in public share and in folders (createdbylib & createdbysandy).
- Lists the sambadeleted directory which is empty. Then we delete the directories using lib and sandy mapped shares.
- Lists samabadeleted folder once again. Now we can see the files deleted by users are moved to the recycle folder under the username directory.
Complete smb.conf file
Samba Swat
Samba swat allows a Samba administrator to configure the complex smb.conf file via a Web browser. Samba swat is a xinetd service which is relatively simple to configure.
Prerequisites
- Allow swat default port 901 through IPTABLES
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 901 -j ACCEPT
Installation & Configuration
- Install samba-swat and xinetd rpms.
# yum install samba-swat xinetd
2. Edit /etc/xinetd.d/swat with following details
service swat { port = 901 socket_type = stream wait = no only_from = 127.0.0.1 10.0.0.0/24 192.168.10.0/24 ##the networks from you need to access swat page user = root server = /usr/sbin/swat log_on_failure += USERID disable = no }3. Star the service and flag it for automatic restart on sever reboot.
# service xinetd start
#chkconfig –add 35 xinetd
4. Point the browser to IP address or FQDN of samba server at port 901 and provide servers username/password as credentials.
Samba useful Information’s.
Refer to